Organizations are constantly seeking innovative solutions to organize their operations and improve efficiency. One of the decisions businesses face is choosing the right Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system to manage their core functions.
However, with the rise of cloud computing, businesses now have a choice between two seemingly similar options: SaaS ERP and Cloud ERP. Both models use the same technology to offer businesses a range of functionalities, yet they differ significantly in terms of deployment, management, and customization.
Understanding the distinctions between SaaS ERP and Cloud ERP is important for businesses to make an informed decision that aligns with their specific needs and objectives. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive comparison of SaaS ERP and Cloud ERP, highlighting their key features, differences, and factors to consider when choosing the best fit for your organization.
What Is SaaS ERP?
SaaS ERP (Software as a Service Enterprise Resource Planning) is a type of Cloud ERP offered through a subscription model on the cloud. SaaS ERP allows businesses to manage their core processes, such as finance, supply chain, manufacturing, services, and human resources.
With SaaS ERP, companies pay a recurring fee to access the software over the internet, eliminating the need for on-premises hardware and software installation. The vendor is responsible for maintaining, updating, and securing the system, ensuring that businesses always have access to the latest features and functionalities.
SaaS ERP offers scalability, allowing organizations to easily adjust their usage based on changing needs. It provides a cost-effective, flexible, and accessible solution for companies looking to streamline their operations and improve efficiency.
What Is Cloud ERP?
Cloud ERP refers to any ERP system hosted on a cloud platform, including SaaS, Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). It offers the flexibility to choose between public, private, or hybrid cloud deployment.
Unlike traditional ERP systems that require installation on local servers, Cloud ERP is hosted on remote servers and accessed through a web browser. This model offers greater flexibility, scalability, and cost savings, as businesses don’t need to invest in hardware or manage software updates and maintenance.
Cloud ERP solutions can be customized to fit the unique needs of a company and are easily scalable to accommodate growth. They also provide real-time data access from anywhere, enabling better decision-making and increased collaboration among teams.
Key Differences Between SaaS ERP And Cloud ERP
While both SaaS ERP and Cloud ERP are cloud-based, they have different characteristics that cater to different business needs.
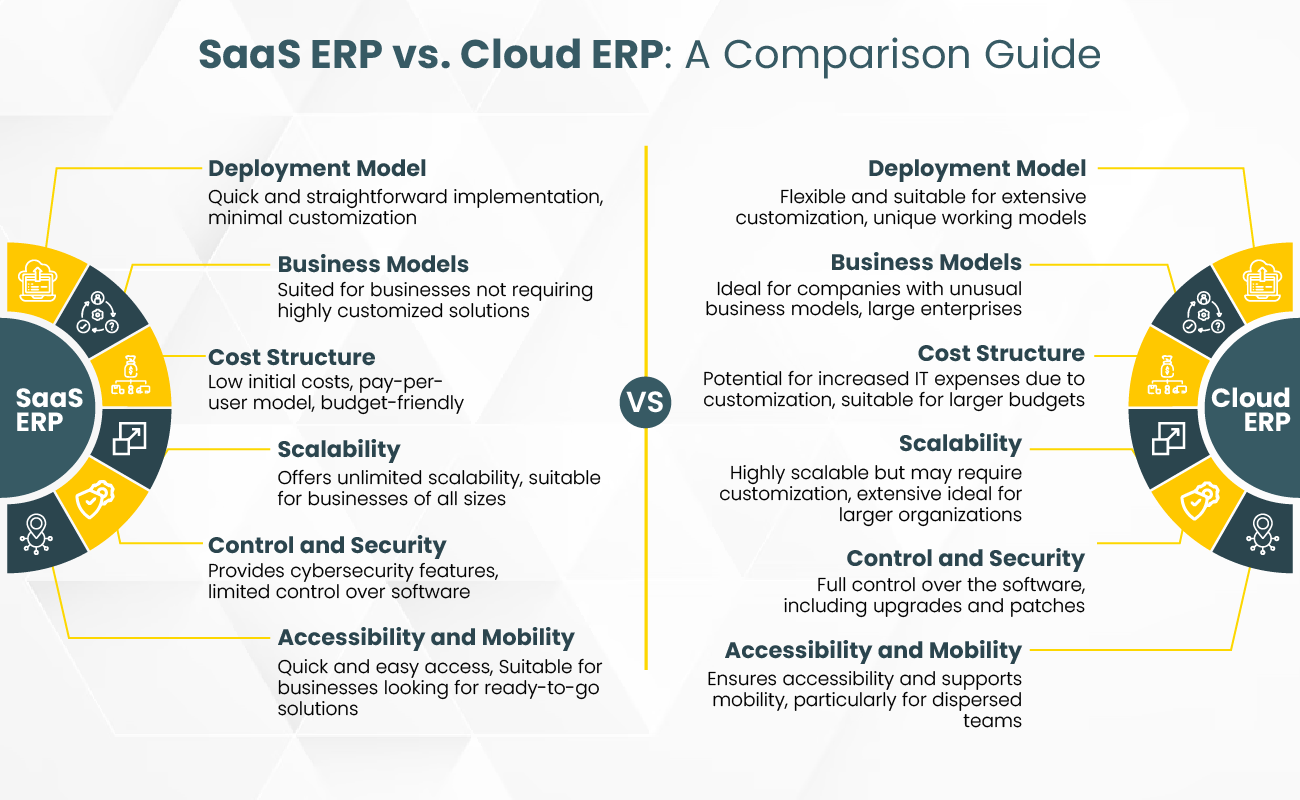
Deployment Model
SaaS ERP: SaaS ERP solutions are designed for quick and easy implementation. They are typically pre-configured and ready to use. This makes them ideal for businesses looking for a rapid deployment of their ERP system. The simplicity of the setup process allows companies to get up and running with their new system in a relatively short amount of time reducing the downtime and disruption often associated with ERP implementations.
Cloud ERP: Cloud ERP offers more flexibility in deployment compared to SaaS ERP. Businesses can choose between public, private, or hybrid cloud options, depending on their needs and preferences. This flexibility allows for a more tailored approach enabling companies to customize their ERP system to fit their unique processes and requirements. The ability to configure the system to specific business needs makes Cloud ERP a preferred choice for organizations with complex operations or unique industry demands.
Customization And Control
SaaS ERP: SaaS ERP solutions are generally less customizable than Cloud ERP. They are designed to meet the needs of a wide range of businesses, which means they may not offer the same level of flexibility for specific industry requirements or unique business processes. Additionally, control over the software is limited, as the vendor is responsible for managing updates and maintenance. This can be a drawback for companies that require a high degree of customization or need to maintain control over their ERP system.
Cloud ERP: Cloud ERP provides greater flexibility for customization, allowing businesses to tailor the software to their specific needs. This can include custom workflows, fields, reports, and integrations with other systems. Greater control is also a key feature of Cloud ERP, as companies can choose when to implement updates and can manage the system according to their own IT policies. This level of customization and control is particularly beneficial for businesses with complex processes or those operating in specialized industries.
Scalability
SaaS ERP: One of the major advantages of SaaS ERP is its scalability. Businesses can easily add or remove users, modules, or features as their needs change. This flexibility makes SaaS ERP an attractive option for growing companies or those with variable demands. The ability to scale the system without significant IT involvement or additional hardware investments is a key benefit of the SaaS model.
Cloud ERP: Cloud ERP is also scalable, but the process may involve more complexity, especially for highly customized systems. While businesses can still scale their ERP system to accommodate growth, this may require additional work. However, the flexibility to tailor the system to specific business needs means that Cloud ERP can provide a more targeted solution for scaling, which can be particularly valuable for larger enterprises or companies with unique operational requirements.
Data Security
SaaS ERP: In a SaaS ERP model, the vendor is responsible for data security which can be both an advantage and a disadvantage. On one hand, businesses benefit from the vendor’s expertise and resources dedicated to security measures. On the other hand, they must rely on the vendor’s ability to protect their data, which can raise concerns about data sovereignty and compliance with industry-specific regulations.
Cloud ERP: With Cloud ERP, businesses have more control over their data security. They can implement their security protocols, choose where their data is stored, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. This level of control is particularly important for companies in sectors with strict data privacy and security requirements. However, it also means that the business is responsible for managing and maintaining these security measures.
Integration Capabilities
SaaS ERP: SaaS ERP solutions may have limitations when it comes to integration with other systems, especially if they are not part of the vendor’s ecosystem. While many SaaS ERP vendors offer APIs and integration tools, there may be constraints on the depth and flexibility of these integrations. This can be a challenge for businesses that rely on a diverse set of software applications and need seamless data flow between them.
Cloud ERP: Cloud ERP systems generally offer more strong integration capabilities compared to SaaS ERP. They can be more easily customized to integrate with a wide range of external applications, databases, and services. This flexibility is important for businesses with complex IT landscapes or those looking to leverage data from multiple sources.
Accessibility And Mobility
Both SaaS ERP and Cloud ERP offer remote access and mobility, allowing users to access the system from anywhere with an internet connection. However, the ease of access and user experience may vary depending on the vendor and the specific ERP solution.
Which Is More Cost-Effective: SaaS ERP or Cloud ERP?
The cost-effectiveness of SaaS ERP vs. Cloud ERP depends on a business’s specific needs and circumstances.
Cloud ERP can be more cost-effective for larger enterprises or businesses with complex processes that require extensive customization. While the initial costs may be higher, the long-term savings from scalability, operational efficiencies, and customization can outweigh the upfront investment.
On the other hand, SaaS ERP is often more cost-effective for small to medium-sized businesses due to its lower upfront costs and predictable subscription-based pricing model. It eliminates the need for significant capital investment in hardware and software, making it an attractive option for companies with limited IT budgets.
Ultimately, the choice between SaaS ERP and Cloud ERP should be based on a careful evaluation of both the immediate and long-term financial implications for the business.
Market Share Of SaaS ERP And Cloud ERP
The cloud ERP market is also on an upward trend, with its global market size valued at $43.60 billion in 2022. The market is expected to witness robust growth, reaching $140.14 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 15.9% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is driven by the rising demand for cloud-based solutions that offer flexibility, improved security, and the ability to integrate with other cloud services, catering to the needs of larger enterprises and organizations with complex processes.
The SaaS-based ERP market is experiencing significant growth, with projections indicating an 11.6% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2023 to 2027. This growth trajectory suggests that the market size will reach an impressive $87.3 billion by 2027. The increasing adoption of SaaS ERP solutions can be attributed to their cost-effectiveness, scalability, and ease of implementation, making them particularly appealing to small and medium-sized businesses.
The Potential Drawbacks or Limitations of Each Model
Both Cloud ERP and SaaS ERP models have their potential drawbacks and limitations:
SaaS ERP Drawbacks:
- Limited Customization: SaaS ERP solutions are typically designed to cater to a broad audience, which can limit the extent to which they can be customized to fit specific business needs.
- Dependence on Vendor: Businesses using SaaS ERP rely heavily on the vendor for software updates, security, and maintenance, which can lead to concerns about control and flexibility.
- Data Security Concerns: While SaaS ERP providers generally offer robust security measures, some businesses may have concerns about storing sensitive data off-site and the potential for data breaches.
- Performance and Downtime: Since SaaS ERP systems are accessed over the Internet, performance can be affected by network issues, and there may be concerns about downtime due to vendor maintenance schedules.
- Long-Term Costs: While the subscription-based pricing model of SaaS ERP can be attractive initially, the ongoing costs can add up over time, especially as a business scales.
Cloud ERP Drawbacks:
- Higher Initial Costs: Cloud ERP systems often require a larger upfront investment for customization, integration, and implementation compared to SaaS ERP solutions.
- Complexity: The increased flexibility and customization options of Cloud ERP can lead to more complex implementations, which may require more time and resources.
- IT Resources: While Cloud ERP offers more control, it also requires a business to have the necessary IT expertise and resources to manage and maintain the system.
- Security and Compliance: Businesses have more responsibility for ensuring data security and compliance with regulations, which can be challenging without the right expertise.
- Scalability Costs: Although Cloud ERP systems are scalable, significant customizations might require additional investments as the business grows or changes.
Which Model Works Better For Businesses?
Small Businesses:
SaaS ERP is generally better suited for small businesses due to its:
- Lower Upfront Costs: SaaS ERP solutions typically have a subscription-based pricing model, which means lower initial investment and predictable monthly or annual fees.
- Ease of Implementation: SaaS ERP systems are usually quicker and easier to deploy since they come pre-configured and require minimal customization.
- Reduced IT Burden: With the vendor handling maintenance, updates, and security, small businesses with limited IT resources can still benefit from a comprehensive ERP system.
- Scalability: SaaS ERP allows small businesses to easily scale their operations by adding or removing users and features as needed.
Larger Enterprises:
Cloud ERP is often more suitable for larger enterprises because of its:
- Customization and Flexibility: Cloud ERP systems offer greater customization options, allowing larger businesses to tailor the software to their complex processes and unique requirements.
- Control and Security: Enterprises have more control over their ERP system, including data security and compliance, which is crucial for businesses with stringent regulatory requirements.
- Integration Capabilities: Cloud ERP can be more easily integrated with other enterprise systems and third-party applications, providing a seamless flow of data across the organization.
- Scalability for Growth: While both models are scalable, Cloud ERP can better accommodate the extensive growth and international expansion of larger enterprises.
Implementation Timeline For SaaS ERP And Cloud ERP
The typical implementation timeline for SaaS ERP and Cloud ERP can vary depending on the complexity of the business processes, the extent of customization required, and the size of the organization.
SaaS ERP: The implementation of SaaS ERP systems is generally faster, ranging from a few weeks to a few months. This is due to the pre-configured nature of the software and the limited customization options available.
Cloud ERP: The implementation timeline for Cloud ERP systems can be longer, often taking several months to over a year. This is because Cloud ERP offers more flexibility and customization options, which can require additional time for configuration, integration, and testing to ensure the system meets the specific needs of the business.
How To Choose SaaS ERP Between Cloud ERP
Choosing between SaaS ERP and Cloud ERP requires a careful evaluation of your business needs, goals, and resources. Here are some steps to help you make an informed decision:
Assess Your Business Requirements:
Identify your core business processes and the specific functionalities you need from an ERP system. Consider the level of customization and flexibility required to support your operations.
Evaluate Your IT Infrastructure:
Determine if your current IT infrastructure can support a Cloud ERP solution or if a SaaS ERP, which requires less IT involvement, is more suitable. Assess your in-house IT capabilities and willingness to manage and maintain an ERP system.
Consider Your Budget:
Compare the upfront and ongoing costs of SaaS ERP and Cloud ERP, including subscription fees, customization, and maintenance expenses. Consider the total cost of ownership over the expected lifespan of the ERP system.
Analyze Scalability Needs:
Evaluate how quickly your business is expected to grow and the scalability requirements of your ERP system. Determine if the flexibility to add or remove users and functionalities is crucial for your operations.
Examine Security And Compliance Requirements:
Assess the data security and compliance needs of your business, especially if you operate in a regulated industry. Determine if you need more control over security measures, which Cloud ERP may offer, or if the vendor-managed security of SaaS ERP is sufficient.
Consult With ERP Experts:
Seek advice from ERP consultants or vendors who can provide insights into the pros and cons of SaaS ERP and Cloud ERP for your specific business context. Request demos and case studies to better understand how each option would work for your organization.
Make A Decision:
Based on your assessment, choose the ERP model that aligns with your business objectives, offers the functionalities you need, fits your budget, and can grow with your company.
Which Is The Right Choice: SaaS ERP And Cloud ERP
The right choice between Cloud ERP and SaaS ERP depends on your business’s specific needs, budget, and IT capabilities.
Cloud ERP is better suited for larger organizations or those with complex processes that require more customization and control. It provides the flexibility to choose between private, public, or hybrid cloud deployment. SaaS ERP, on the other hand, is ideal for small to medium-sized businesses seeking a cost-effective, easy-to-deploy solution with minimal IT overhead.
While both options offer advantages and some limitations, understanding your business requirements and proper guidance from NetSuite Implementation experts is key to making the right decision. Selecting the ERP solution that aligns with your organization’s goals and growth trajectory is important for long-term success.
For small and medium-sized businesses on the lookout for the right ERP solution, NetSuite is a game-changer. And the best part? It grows with you, offering real-time insights that help you make smart decisions. We, at VNMT Solutions, specialize in customizing NetSuite to meet the unique needs of small and medium-sized businesses. Contact us today and talk to experts!